Manufacturing Process
-
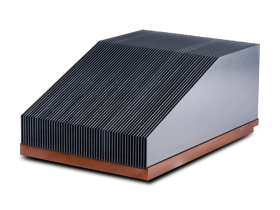
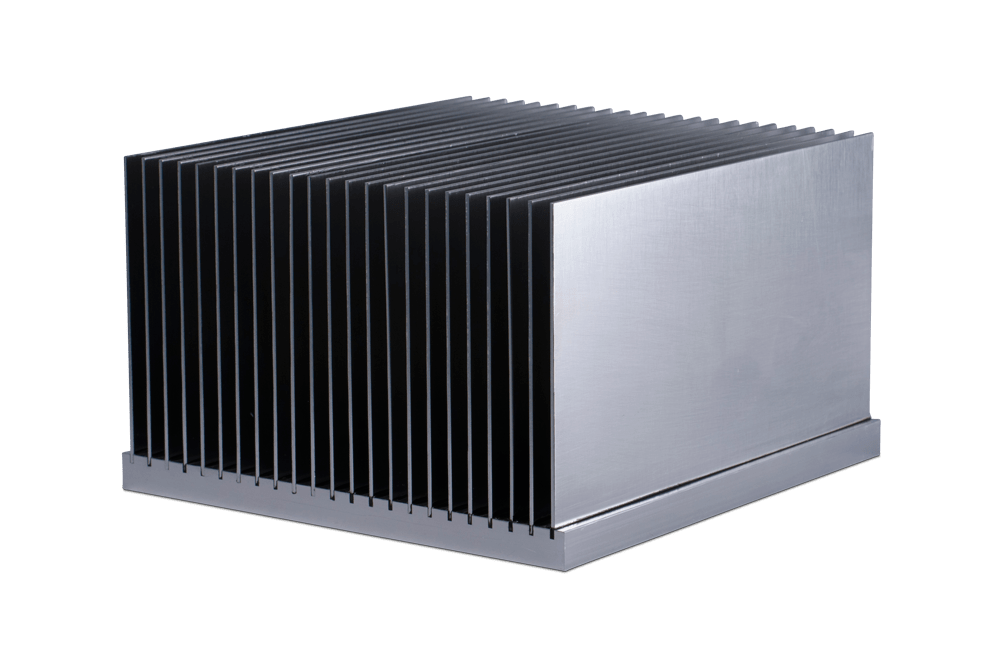
Bonded fin heat sinks are manufactured using an assembly process that involves bonding a layer of thin metal fins to a base or substrate. The following is the general process for manufacturing bonded fin heat sinks:
Preparation: The base and fins are typically made from aluminum or copper and are carefully cleaned to ensure that the bonding process will be successful.
Bonding: The fins are then bonded to the base using an adhesive material, such as epoxy or a thermal transfer compound. The adhesive material is typically applied to the base in a uniform manner, and then the fins are placed on top and pressure is applied to ensure a strong bond.
Curing: The adhesive material is then cured, usually by heat or UV light, to create a permanent bond between the fins and the base.
Assembly: If the heat sink requires additional components, such as mounting hardware or interface material these are attached at this stage.
This process can be automated for high volume production or performed manually for smaller runs. The choice of materials, bonding method, and assembly process will vary based on the specific requirements of each application, but the general process remains largely the same.
Materials
-
Base material: 6063-T5 aluminum
-
Fin material: 1100-H14 aluminum
Specifications
-
24 in (609 mm) max profile width
-
>/= 0.4 mm fin thickness
-
30:1 fin height to minimum gap ratio and greater
-
>/= 4 mm base thickness
Applications
-
Uninterruptible power supplies
-
Variable speed motor controls
-
TECs
-
Motor drives
-
Forced air
-
Industrial
Benefits
-
Increases the cooling surface area by 2 to 3 times (higher aspect ratio of fins)
-
Dissipates more heat than conventional heat sinks with same footprint
-
Reduces heat sink and overall system volume
Tooling Cost
Production Cost
Finishing
- CNC machining
- Drilling
- Tapping
- Stamping
- Anodizing
- Screen printing
- Powder coating
- Laser etching
- Polishing
- Embedded fans
- Thermal greases
- Screws
- Springs
- Clips
- Embedded heat pipes
- Phase change materials
- Back plates
- Gap filler pads
- PEMS
- Standoffs
- Dielectric pads
- Compounds