Description
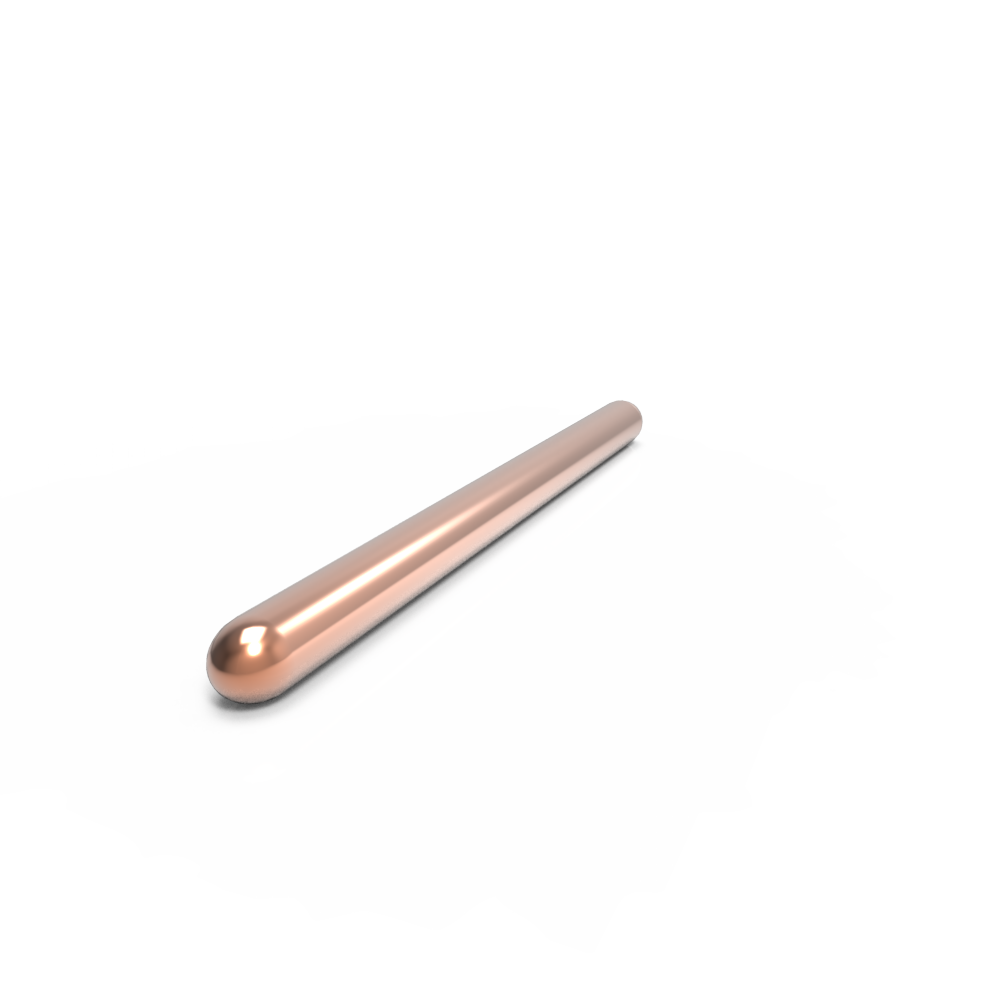
A heat pipe is a type of passive heat transfer device commonly used for electronic cooling. It is a closed container typically made of copper and filled with a small amount of working fluid.
The heat pipe works by transferring heat from one end to the other, using the phase change of the working fluid. When the heat source heats the evaporator section of the heat pipe, the working fluid inside evaporates and becomes a vapor. The vapor then travels to the cooler end of the pipe (the condenser section), where it condenses back into a liquid, releasing the heat it absorbed along the way. The liquid then flows back to the evaporator through a wick structure or capillary action, completing the cycle.
Heat pipes can efficiently transport large amounts of heat with minimal temperature differences between the hot and cold ends, making them a popular choice for electronic cooling applications. They are also lightweight, compact, and have no moving parts, making them reliable and low maintenance. Heat pipes are commonly used in laptops, gaming consoles, LED lighting, and other electronic devices that require efficient cooling.